Air Source Heat Pumps
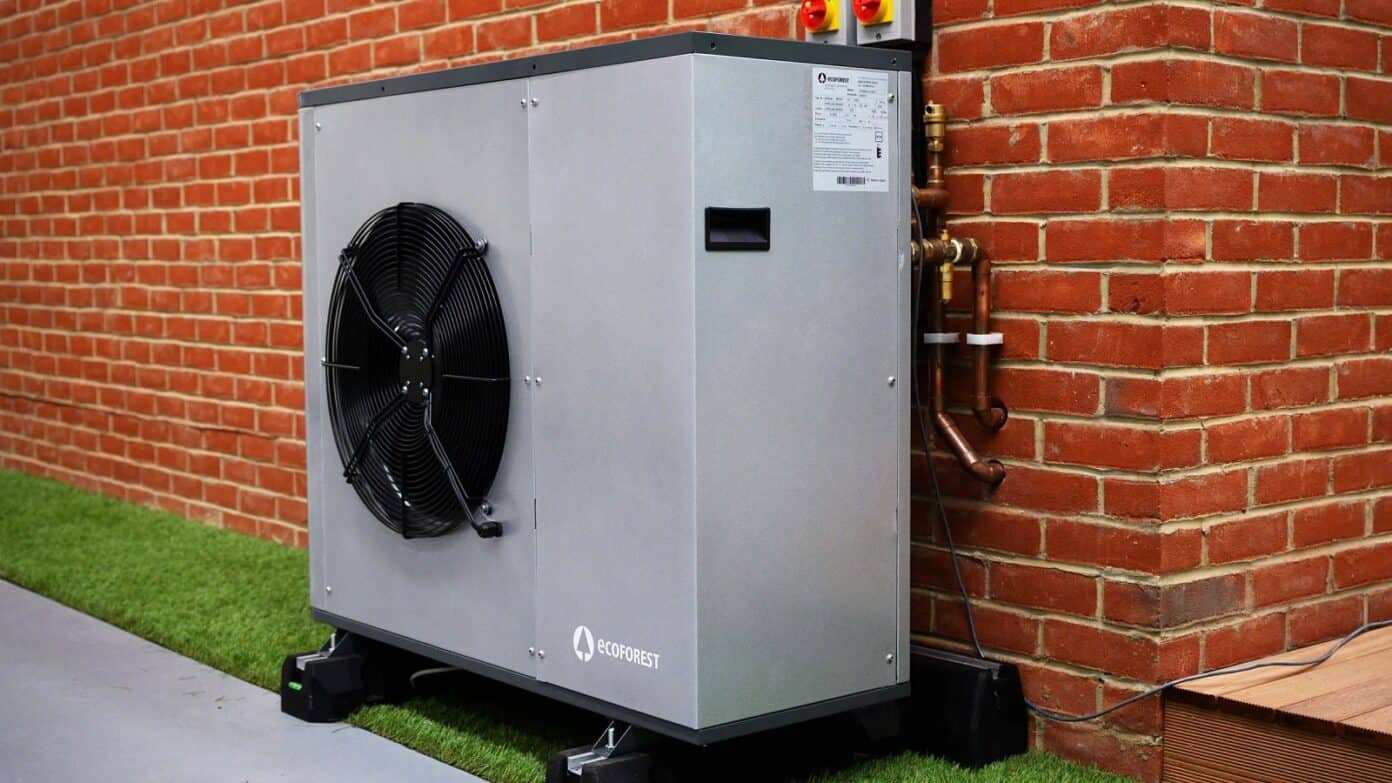
Air source heat pumps extract energy from the surrounding air, a renewable resource, to provide heating and hot water. This reduces reliance on non-renewable energy sources, helping to lower your carbon footprint.
How Do Air Source Heat Pumps Work?
Air source heat pumps absorb heat from the outside air. Unlike conventional heating systems like boilers, these pumps transfer heat to radiators, underfloor heating, and hot water systems in your home. The heat extracted from the air is continuously replenished, contributing to a lower carbon footprint. Air source heat pumps deliver a consistent, ambient temperature throughout the home, as opposed to direct heat from isolated sources like radiators.
The Boiler Upgrade Scheme (BUS)
is a financial incentive offered by the UK government to promote renewable heat technologies. This grant provides up to £7,500 towards the purchase and installation of air source heat pumps. By transitioning to renewable energy systems, you can contribute to reducing carbon emissions and helping the UK meet its renewable energy targets. For more details on the BUS scheme, visit Ofgem’s website.
Air source heat pumps operate using technology similar to refrigerators and air conditioners. They extract heat from the air, ground, water, or industrial waste heat, then transfer it efficiently to your home. Because they transfer heat rather than generate it, air source heat pumps are significantly more energy-efficient than traditional systems like boilers and electric heaters, often reducing running costs. The typical coefficient of performance (COP) for household heat pumps is around 4, meaning the energy output is four times greater than the electrical input. Heat pumps can also be combined with existing systems like gas boilers in hybrid setups.
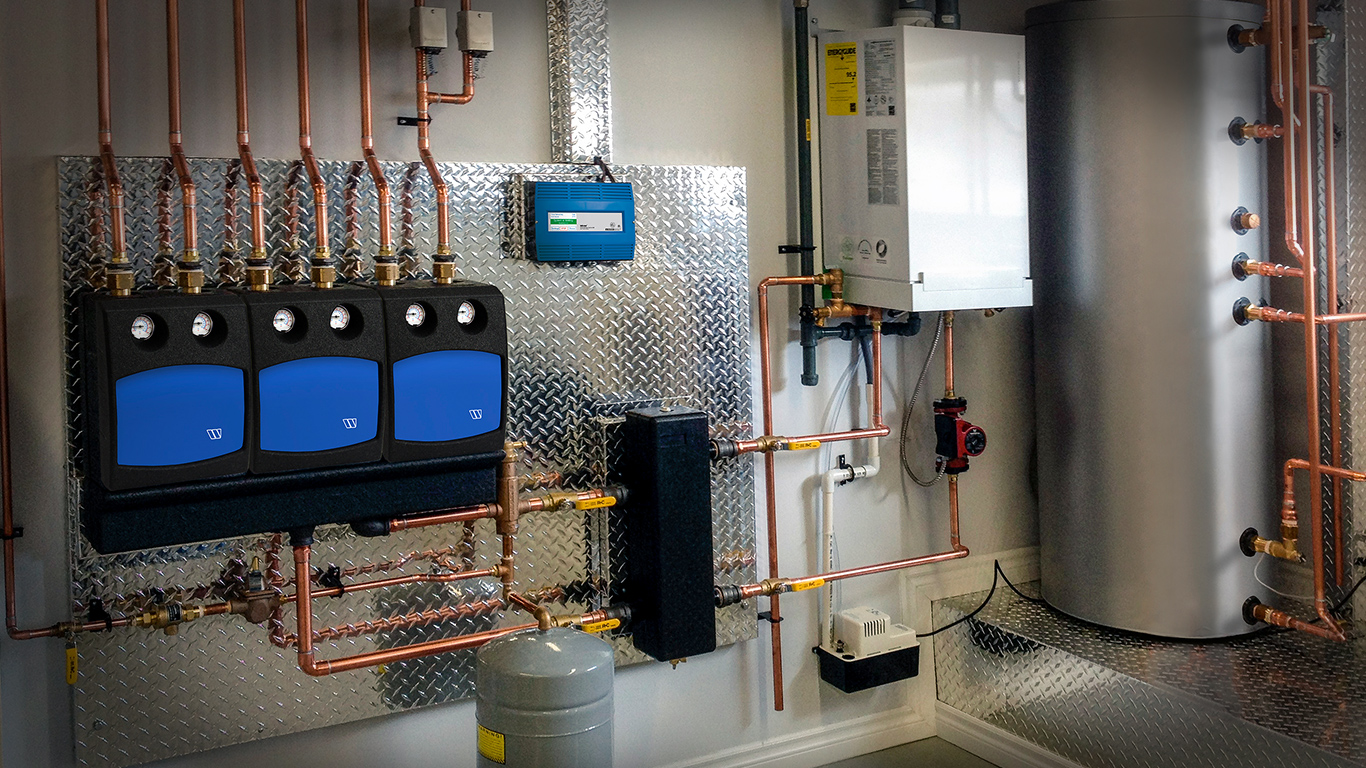
The heat pump system consists of a compressor that circulates refrigerant through a cycle, a heat exchanger to extract heat, and a heat sink to transfer it. In buildings, heat is delivered through hydronic systems like radiators or underfloor heating. In addition to heating, many air source heat pumps provide cooling in the summer. In industrial applications, they are used for processes like delivering hot air, water, steam, or heating materials, particularly in district heating networks or commercial settings.